前言
尝试复现 RePr: Improved Training of Convolutional Filters 中,做个记录。
完整 code 见 GitHub: RePr
介绍
详细的看论文啊,这里简单带过。
目标
- 调整训练流程来避免 filters 间的 overlap。
效果
- 在很多实验都能提升准确率。
方法
- S1 stage 结束时以作者提出的 inter-filter orthogonality(将 filters 各 flatten 成一维向量,计算每个 filter 与其他 filters 的向量内积之和)为评分标准,将正交性较差的进行剪枝。
- S2 stage 过程只以剩下的 filters 进行训练,最后再将被剪枝的 filters 重新初始化训练。
-
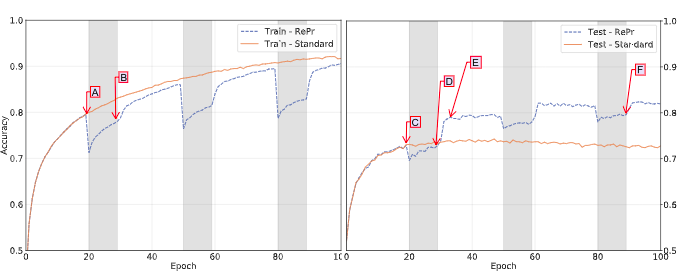
白色区:S1 stage 灰色区:S2 stage
基本做法
目前以 masking 的方式来实现。
S1 stage
- S1 stage 结束时以 inter-filter orthogonality 选出不好的 filters 将 weights 设为 0。
S2 stage
- 每次更新参数时把 pruned filters 的 gradient 设 0,确保过程中被 prune 的这些 filter 都还是全 0。
- 结束时对 pruned filters 进行 reinitialize,并把这些 filters 下一层对应的 weights (channels) 也设 0(这部分还不确定)。
Reinitialize 阶段论文里不清楚的细节 + Reddit 私讯作者的补充
- Null space vectors 数量不够用来初始化?
- 对 $C^3(32)$ 的模型来说,第一层有 32 个 filters,每个 filter 的参数量(若 kernel size 为 3x3)是3x3x3,这样一来 flatten 之后的矩阵是32x27,null space 是空集,没有正交的 filter。
- 作者:
You can relax the requirement that the new filter has to be orthogonal to all the filters. There is no proper heuristics, but you can use orthogonal ranking to find the most overlapping ones and only use those to compute the re-initialization
- 目前做法:以 PyTorch 预设初始 conv2d weights 的方式初始化。source
- Null space vertor 与 filter 的对应关系?
- QR decomposition (或其他方法)找到 null space 之后怎么利用这些正交的向量来对 filter 进行 reinitialize ?(如何 scaling 之类的)
- 作者:
Yes, random vectors in the null space. Scale of this vector becomes important when you are dropping large percentage of filters. I tried various things including projecting the norm. However, I was running short on time thus I did a quick experimental thing that is clip the weights to be some upper-bound (if x > LIM then x = LIM).
- 目前做法:不做 scaling ,直接把 QR decomposition 找到的任意正交向量经过 clip 后当成 filter。
实验
数据集:CIFAR-10
模型:vanilla cnn $C^3(32)$
 |
论文结果
| Std | RePr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72.1 | 76.4 |
目前结果
实验设定:
- general:100 epochs, learning rate = 0.01
- RePr 超参:S1 = 20, S2 = 10, prune-ratio = 0.3
| Std | RePr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77.84 | 74.48 |
加上 tensorboardX 视觉化:
| Standard vs. RePr | Filters on/off map |
 |
 |
与论文结果对比:

不同点
- training acc 曲线比较接近,但 reinitialize 之后没特别明显的回升。
- 论文有明显的 overfitting。
- 倾向于 prune 浅层的 filters,知乎上也有人遇到同样的问题。
其他尝试
Overfitting?
论文曲线 train acc 最终在 90% 左右,test acc 在 70% 左右,有较严重的 overfitting。但我们的 train acc 甚至比 test acc 略低,这是 PyTorch 的 data augmentation torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop 带来的影响。若不做 random crop,则 training acc 会直接接近 100,testing acc 60++。(详见下面的实验结果)

若将 learning rate 调小至 0.003,epoch 数增加,可以观察到 RePr 确实带来一些 generalization 的效果。
| Standard vs. RePr | Filters on/off map |
 |
 |
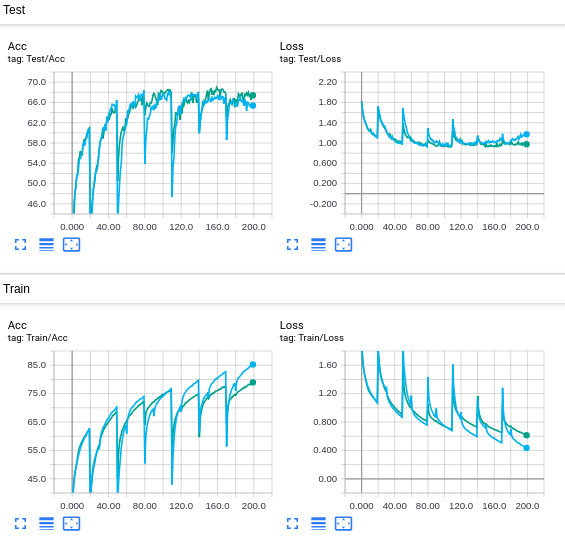
但同样的实验设定下,用上 random crop 的结果明显更优。
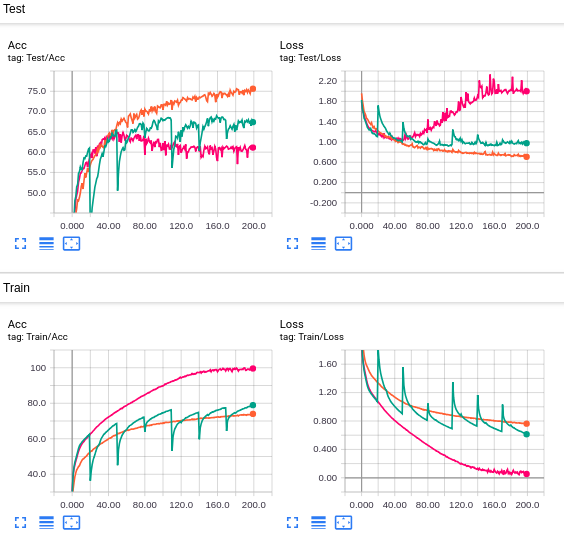
Zero-initialization or Random-initialization?
将 filters prune 了之后,下一层与其相接的参数该怎么初始化,这是论文里面没详细描述的。这里尝试了两种不同初始化方法的结果:
| zero-initialization vs. random-initialization | zero map | random map |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
在 re-initalize 阶段,random-initialization 有较明显的掉点,但之后会有较快的回升,zero-initialization 反之。
而论文同时集两种初始化好处于一身,re-initialize 不掉点,回升快。
另一个显著的差异是 zero-initialization 的方式会让被 prune filter 的选择往后传,但还是和论文中倾向于较深 filters 的剪枝不太一样。
总之实现上大概还有些不太一样的细节。
反其道而行
尝试对 inter-filter orthogonality 值较低(正交性较佳)的进行剪枝:
| RePr vs. Reverse RePr | RePr | Reverse RePr |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
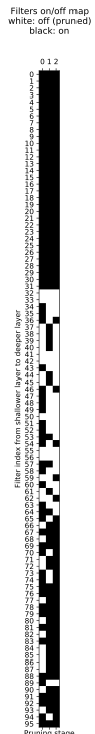 |
Reverse RePr 每次剪枝 acc 越掉越多,因此 inter-filter orthogonality 是有效的。
但可以确定的是 layer 之间的 ranking 肯定还有更公平的比较规则。
思考
目前 RePr 效果不佳可能原因:
- RePr 流程主要提升泛化性,重点在于解决 overfitting
Abstract
…
We show that by temporarily pruning and then restoring a subset of the model’s filters, and repeating this process cyclically, overlap in the learned features is reduced, producing improved generalization.
… - 实验设定有些不同(standard 跑起来并不像论文那样 train acc 90%, test acc 70%)
- 还有一些不清楚的细节(如 layer 之间的 ranking 规则)
- code 有 bug
结语
各方面新手,非常欢迎路过的有缘人给点建议啦!
在此特别感谢热心的网友陆续给我发 GitHub Issues 帮我 debug ( ̄▽ ̄”)